How to exclude internal traffic from Google Analytics
28 Nov 2020
Google Analytics is the web analytics tool I use to track my website traffic. The dashboard was overwhelming to look at first and it has taken a good amount of time for me to understand what certain data points mean.
The types of data I collect on GA are user acquisition dad and user behavior data. This basically gives me a better understanding about my user demographics, where they have landed from and what media channels they frequent. I also understand how long a user has stayed on my website, their entry and exit pages and the most common pathway through which they go through my website.
The user behavior data also serves as a guide for me to improve my website. Well since this is a small website, I get a lot of leeway to experiment and learn about analytics and tracking.
Initially, it was common for me to get a very high number of hits on my website till I realized it was me who was visiting most of the time for a general quality assurance of the website. This impacted the numbers heavily. And that is when I realized I needed to block my internal traffic in order to get the correct data about the users visiting my website.
Also, as the tracking code is added to my local dev environment, there was a high number of hits from my local traffic as well.
Blocking internal traffic on google analytics
Blocking internal traffic generally involves filtering and excluding your IP addresses in google analytics. It took me a couple of tries to finally get it right.
To exclude your IP address from Google Analytics:
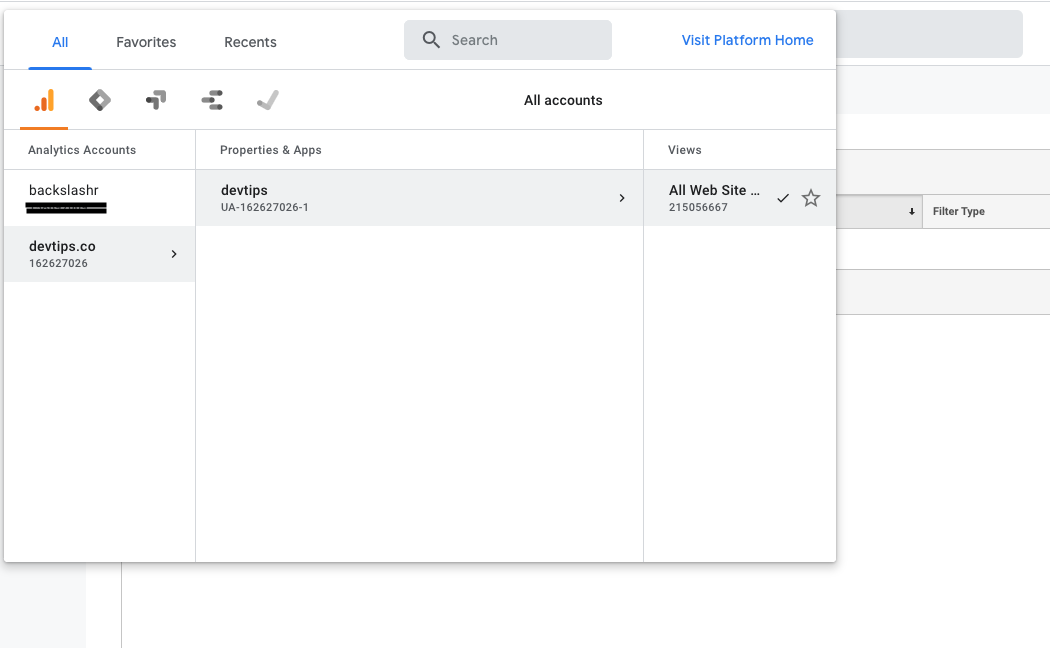
Login and select your profile in Google Analytics.
Select the admin option on the sidebar.
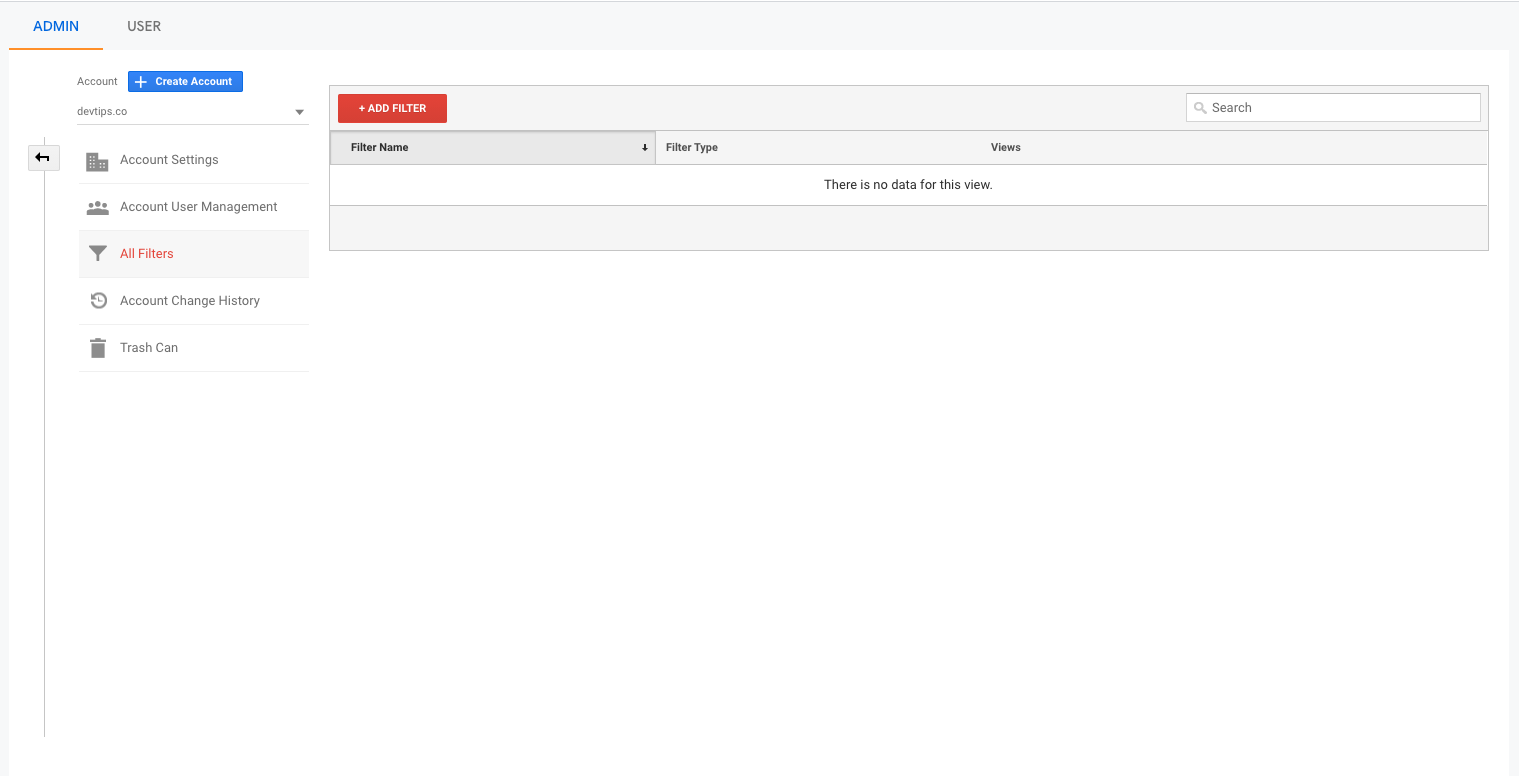
Under account, select all filters and click on add filters.
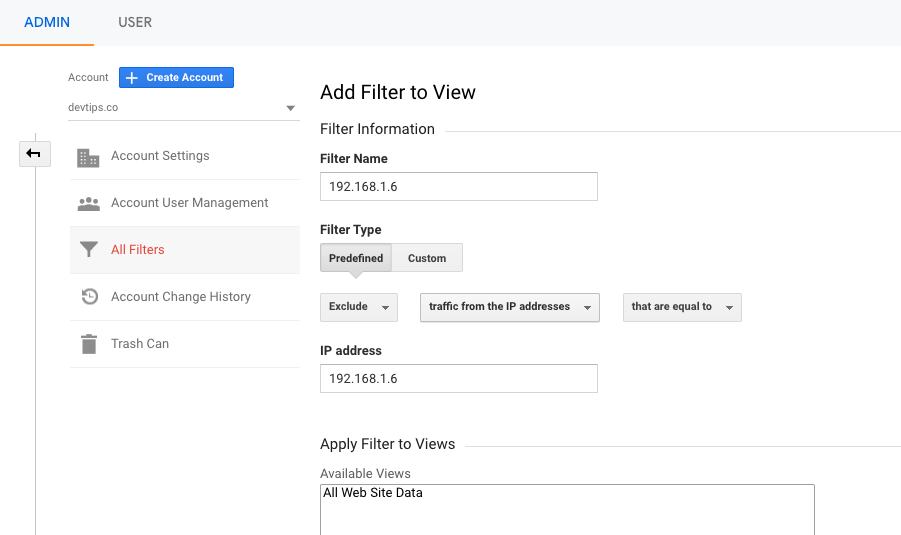
Give a name to the filter. It can be an IP address or the physical location of the traffic source.
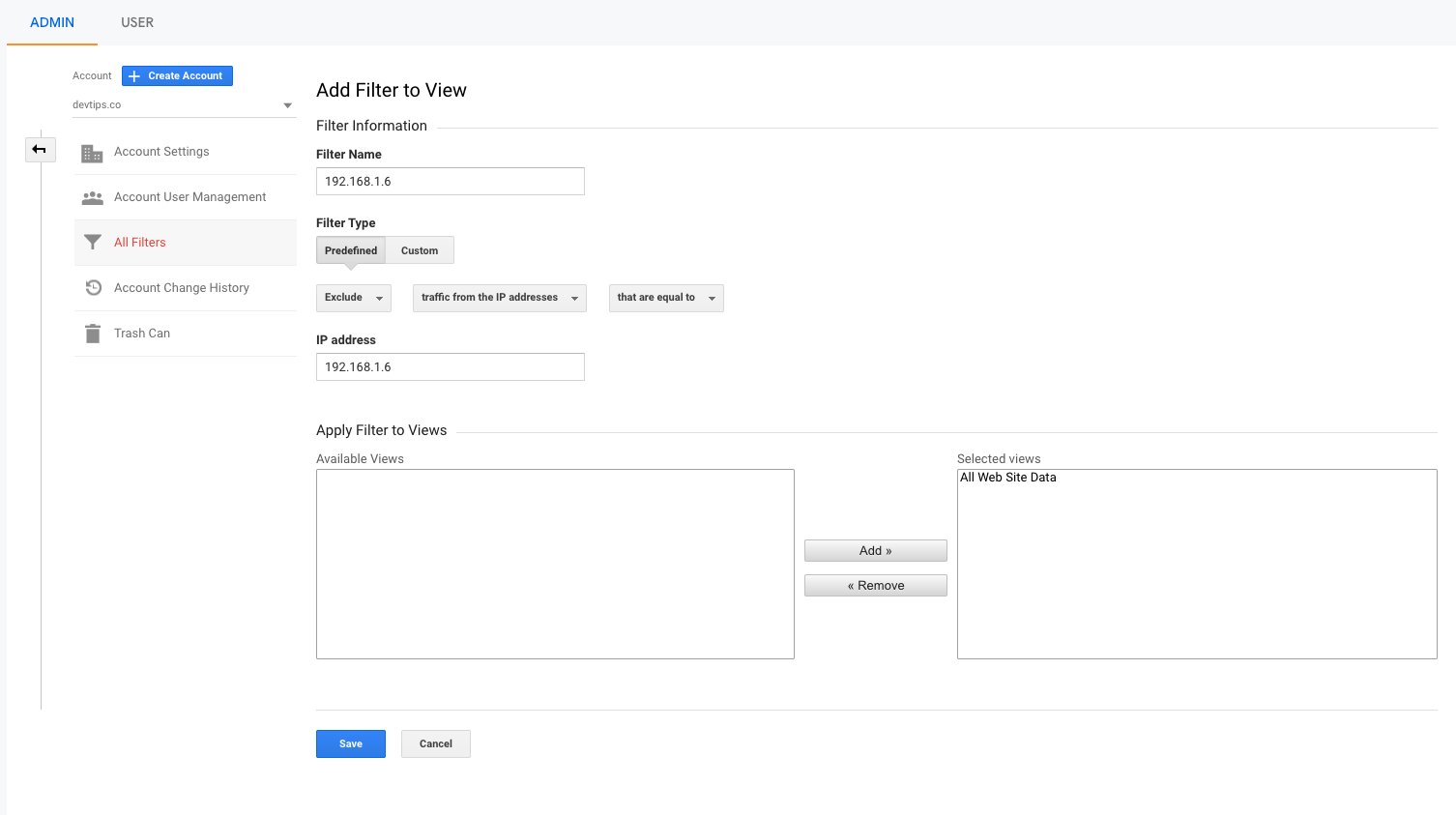
Leave the filter type as predefined.
Then select exclude, traffic from the IP addresses, that are equal to.
Add your IP address in the IP address field.
Select and add All website data inside available views to Selected views.
Save the filter.
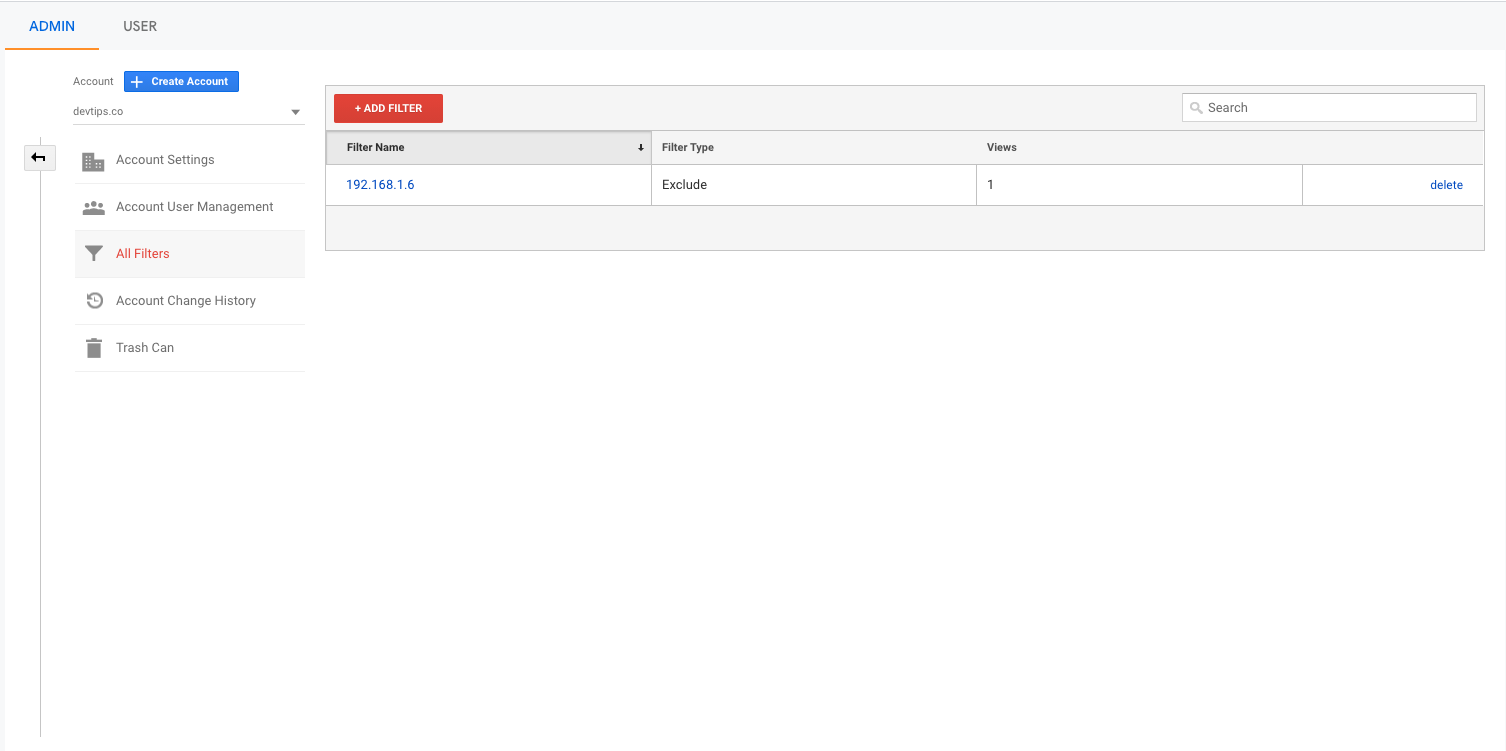
You can now go back to all filters and see the filter listed with the type and views. If you access the website from your internal IP, you'd see the view count updated as well. This is one way to verify if the filter is working.
All historical data will still be polluted with visits from your internal IP address but going forward, visits from your IP address will be excluded. This can be a good starting point to get more accurate data to improve your website.